- MaxiCharger DH480
- MaxiCharger AC Pro
- MaxiCharger DC HiPower
- MaxiCharger DC Fast
- MaxiCharger DC Compact
- MaxiCharger AC Elite

- For CPOs
- For Fleets
- For Destination
- For Residential
 MaxiCharger DH480
MaxiCharger DH480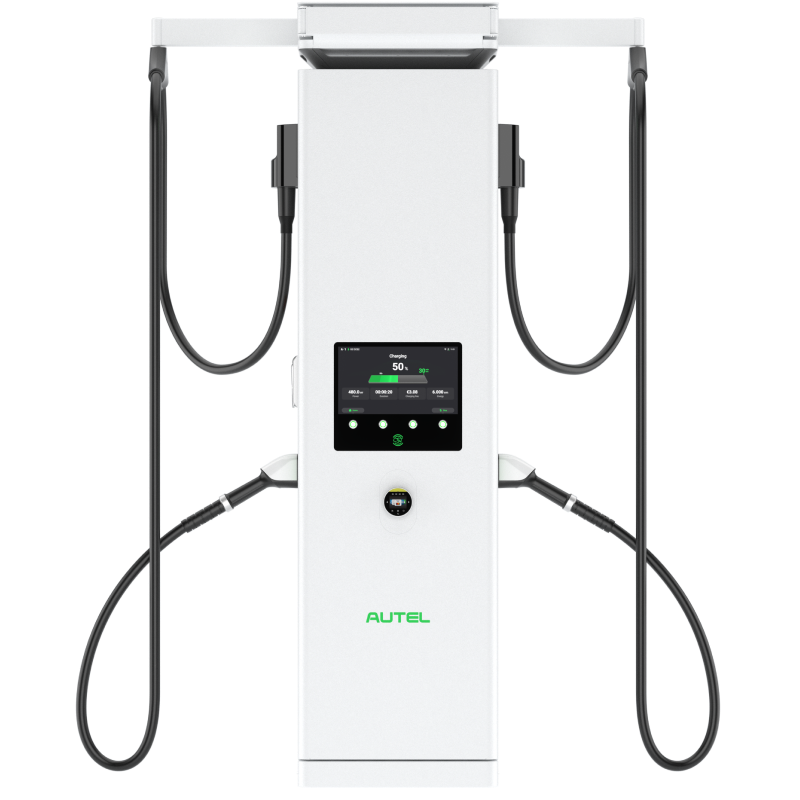 MaxiCharger DC HiPower
MaxiCharger DC HiPower MaxiCharger DC Fast
MaxiCharger DC Fast MaxiCharger DC Compact
MaxiCharger DC Compact
 MaxiCharger AC Pro
MaxiCharger AC Pro MaxiCharger AC Ultra
MaxiCharger AC Ultra MaxiCharger AC Elite
MaxiCharger AC Elite
 Software
Software
- Partner Introduction
- Become A Partner
- Event
- FAQ
- Blog
- About Autel
- Contact Us
- Sustainability
- Newsroom
- Brand Center
- Product Center
What is a level 3 charging station? [2025 Update]

A Level 3 charging station, also known as a DC Fast Charger, is the fastest way to charge an electric vehicle (EV). Unlike slower chargers, it delivers direct current (DC) power directly to the vehicle’s battery, significantly reducing charging time.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Level 3 charging stations work, their benefits, installation requirements, and future trends. Keep reading to learn more about the fast-charging technology shaping the future of electric mobility.
Technical Overview of Level 3 Charging Stations
Power Conversion
Level 3 charging stations change alternating current (AC) from the power grid into direct current (DC). They then send this DC power to an EV’s battery. This process bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger, allowing much faster charging than Level 1 and Level 2 stations.
Voltage and Power Output
These chargers operate at high voltages, typically between 400 and 900 volts, with power outputs ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW. This high power lets EVs gain a lot of range in just a few minutes. Level 3 charging is great for road trips and quick recharges.
Connector Types
Level 3 chargers use different connector standards depending on the vehicle and charging network. The most common include:
- Combined Charging System (CCS) – Standard for most EVs in North America and Europe.
- CHAdeMO – Used mainly by Japanese EVs like Nissan Leaf.
- NACS –NACS (North American Charging Standard), developed by Tesla, is one such connector. Originally proprietary, it became an open standard in 2022, allowing broader adoption by other EV manufacturers.
The Autel EV Charger supports multiple connector standards, including CCS, CHAdeMO, and Tesla Superchargers, ensuring compatibility with most EVs. It delivers up to 480kW of power, significantly reducing charging time for long-distance travel and commercial use. Designed for Supplied worldwide, including North America, Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America. it offers a seamless and efficient charging experience across different networks.
Battery Management System Communication
The charger and the EV's battery management system (BMS) talk to each other in real-time. This helps adjust power flow, stops overheating, and ensures safe charging. This system helps optimize battery life and efficiency.
Cooling System
Fast charging generates heat, so Level 3 chargers often include liquid or air cooling. These cooling systems prevent overheating, ensuring safe operation and maintaining charger performance during prolonged charging sessions.
Installation Requirements
Level 3 chargers require a dedicated electrical infrastructure, often with a 480V three-phase power connection. This high-power requirement makes them unsuitable for home use, and installers mainly place them in public charging networks.
Charging Protocols
Most Level 3 chargers follow Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP), allowing remote monitoring and management. This enables payment processing, user authentication, and smart energy management.
How Level 3 Charging Works
Direct Current (DC) Delivery
Level 1 and Level 2 chargers use alternating current (AC). In contrast, Level 3 chargers provide direct current (DC) power to the EV battery. This eliminates the need for the vehicle’s onboard converter, allowing much faster energy transfer.
Fast Charging Speeds
Level 3 charging significantly reduces charging time compared to slower chargers. The charger’s power and battery size can add 100-250 miles of range in 15-45 minutes. This makes it great for long trips.
Conversion within the Station
The AC-to-DC conversion happens inside the charging station, rather than within the EV. This accelerates charging speeds since the power delivered is already in the correct format for direct battery input.
High Voltage and Power Output
Level 3 chargers operate at much higher voltages, typically between 400 and 800 volts, with some exceeding 900 volts. This high power level enables rapid energy transfer while maintaining efficiency.
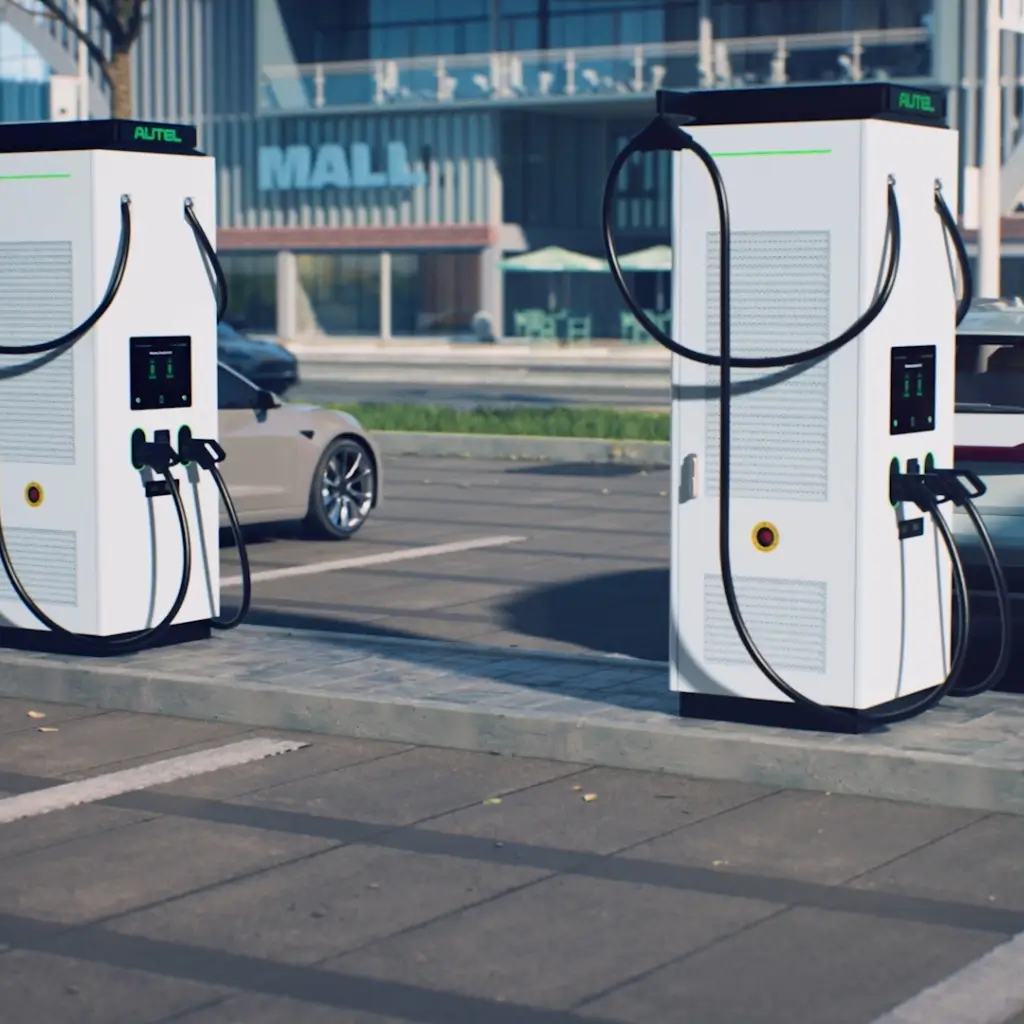

Battery Management Communication
While charging, the station talks to the EV’s battery management system (BMS). This helps control power flow, speed up charging, and protect the battery from overcharging.
Cooling Systems for Heat Management
Fast charging generates heat, so Level 3 chargers often use liquid or air cooling systems. These prevent damage to the charger and the vehicle’s battery, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
Public Charging Station Deployment
Level 3 chargers need a lot of power and can be expensive to install. Because of this, you usually find them in public places. These places include highway rest stops, shopping centers, and fleet charging hubs.
Level 3 Charging Station Advantages and Benefits
Rapid Charging Speeds
Level 3 chargers provide the fastest EV charging option, adding 100-250 miles of range in just 30-45 minutes. This makes them essential for drivers needing a quick recharge.
Convenience for Long-Distance Travel
With faster charging times, EV drivers can complete long trips with fewer stops. They place these chargers along major highways to ensure road trip convenience.
Supports Business Growth
Businesses that install Level 3 chargers attract more customers. Drivers often shop, dine, or visit services while charging, increasing foot traffic and revenue.
Reduces Range Anxiety
Many drivers worry about running out of battery—known as range anxiety. Level 3 chargers help eliminate this concern by providing fast and widely available charging options.
Encourages EV Adoption
By improving charging convenience and reducing wait times, Level 3 stations promote EV ownership, making electric cars more practical.
Enhances Fleet Efficiency
Businesses with electric fleets (e.g., delivery vans, ride-sharing vehicles) benefit from fast charging. Shorter charging times mean less downtime and increased efficiency.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Many Level 3 charging stations now use solar and wind energy. This reduces the need for fossil fuels and supports sustainable EV charging.
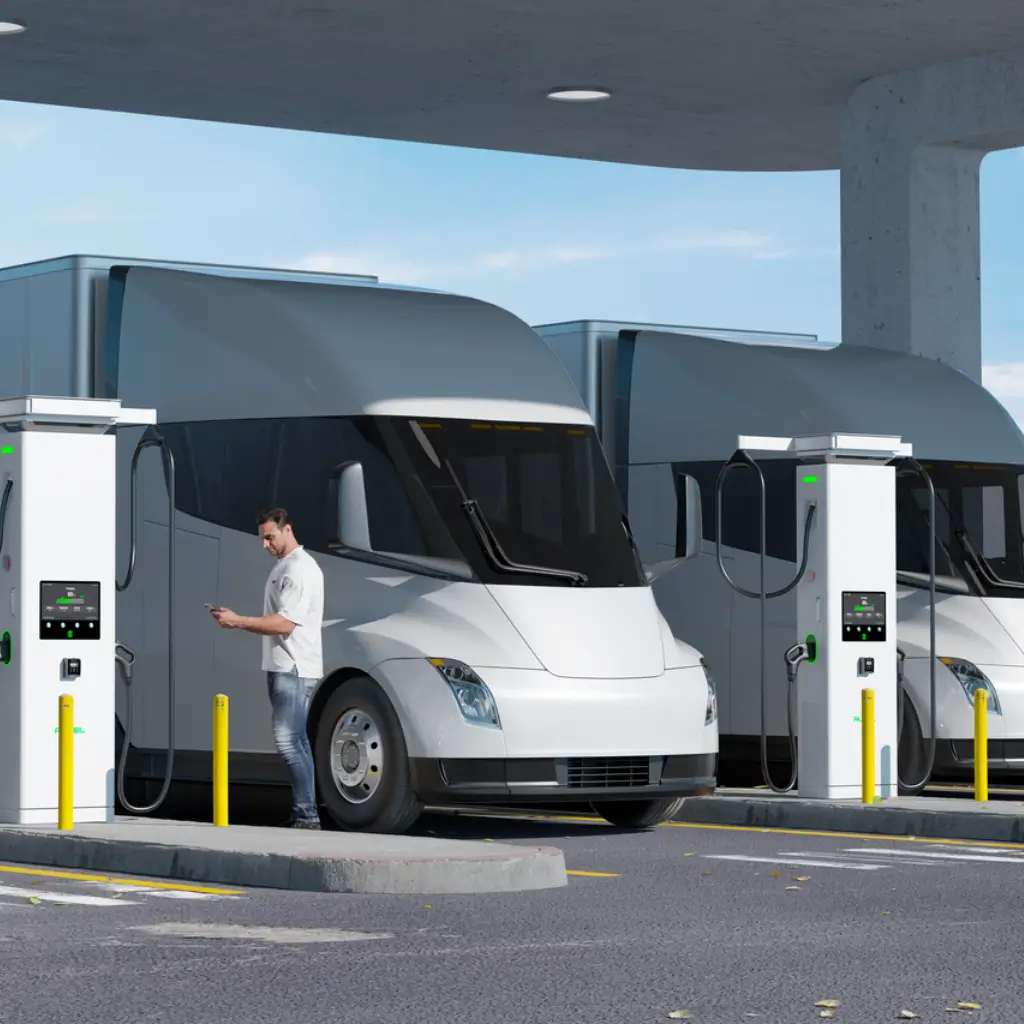

Future Trends in Level 3 Charging
Higher Power Outputs
New Level 3 chargers will be over 350kW. This will let EVs charge in just minutes. Long-distance travel will be even easier.
Standardization Across Networks
EV manufacturers and charging networks are moving toward unified connector standards, such as CCS, simplifying access to fast chargers.
Smart Grid Integration
Future chargers will integrate with smart grids, optimizing energy use and preventing overloads by adjusting power demand.
Expansion of Ultra-Fast Charging Stations
More high-power chargers are being installed along major highways, ensuring faster charging access for long-distance travelers.
Plug-and-Charge Technology
With plug-and-charge, EV drivers will simply plug in and start charging—no apps or cards required, making charging easier.
Bidirectional Charging
Future Level 3 chargers will allow energy to flow both ways. This means EVs can send power back to the grid. This helps keep energy stable.
Improved Affordability
As technology improves, the cost of installing and using Level 3 chargers will go down. This will make them easier for businesses and cities to access.
In Conclusion
Level 3 charging stations are the fastest and most efficient way to charge an EV. They are essential for road trips, businesses, and fleet operations. As EV adoption grows in 2025, these chargers are becoming faster, more available, and smarter.
Understanding fast charging is important. It has benefits and future trends that can help. This knowledge will assist EV owners, businesses, and fleet operators in making smart decisions.



